NSCLC-Radiomics | NSCLC-Radiomics
DOI: 10.7937/K9/TCIA.2015.PF0M9REI | Data Citation Required | 20.5k Views | 131 Citations | Image Collection
| Location | Species | Subjects | Data Types | Cancer Types | Size | Status | Updated | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lung | Human | 422 | CT, SEG, RTSTRUCT, Classification, Diagnosis, Demographic, Follow-Up | Lung Cancer | Clinical, Image Analyses | Public, Ongoing | 2020/10/22 |
Summary
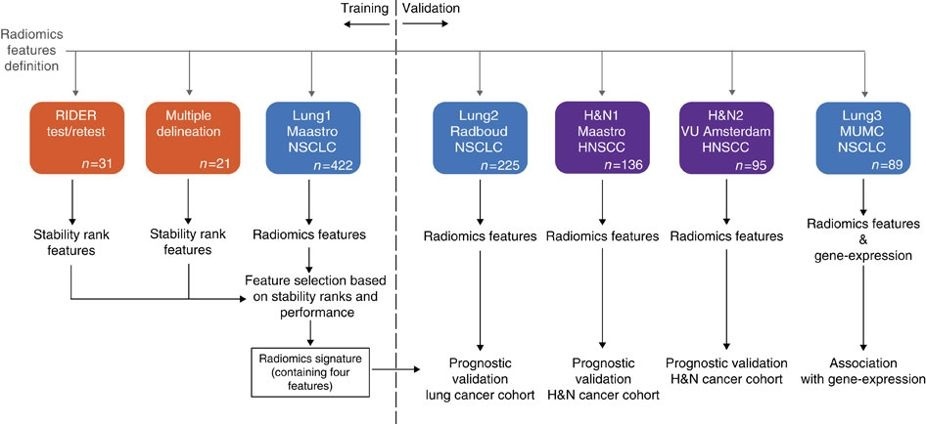
This collection contains images from 422 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. For these patients pretreatment CT scans, manual delineation by a radiation oncologist of the 3D volume of the gross tumor volume and clinical outcome data are available. This dataset refers to the Lung1 dataset of the study published in Nature Communications. In short, this publication applies a radiomic approach to computed tomography data of 1,019 patients with lung or head-and-neck cancer. Radiomics refers to the comprehensive quantification of tumour phenotypes by applying a large number of quantitative image features. In present analysis 440 features quantifying tumour image intensity, shape and texture, were extracted. We found that a large number of radiomic features have prognostic power in independent data sets, many of which were not identified as significant before. Radiogenomics analysis revealed that a prognostic radiomic signature, capturing intra-tumour heterogeneity, was associated with underlying gene-expression patterns. These data suggest that radiomics identifies a general prognostic phenotype existing in both lung and head-and-neck cancer. This may have a clinical impact as imaging is routinely used in clinical practice, providing an unprecedented opportunity to improve decision-support in cancer treatment at low cost. The DICOM Radiotherapy Structure Sets (RTSTRUCT) and DICOM Segmentation (SEG) files in this data contain a manual delineation by a radiation oncologist of the 3D volume of the primary gross tumor volume ("GTV-1") and selected anatomical structures (i.e., lung, heart and esophagus). Of note, DICOM SEG objects contain a subset of annotations available in RTSTRUCT. Other data sets in the Cancer Imaging Archive that were used in the same study published in Nature Communications: Head-Neck-Radiomics-HN1, NSCLC-Radiomics-Interobserver1, RIDER-LungCT-Seg. For scientific or other inquiries about this dataset, please contact TCIA's Helpdesk.
The dataset described here (Lung1) was used to build a prognostic radiomic signature. The Lung3 dataset used to investigate the association of radiomic imaging features with gene-expression profiles consisting of 89 NSCLC CT scans with outcome data can be found here: NSCLC-Radiomics-Genomics.
Data Access
Version 4: Updated 2020/10/22
- RTSTRUCT and SEG study instance UID changed to match study instance uid with associated CT image.
- Added missing structures in SEG files to match associated RTSTRUCTs.
- Patient Id copied to Patient Name in CT images (for consistency).
- Added 1 missing image for LUNG1-246.
| Title | Data Type | Format | Access Points | Subjects | License | Metadata | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Images, Segmentations, and Radiation Therapy Structures | CT, SEG, RTSTRUCT | DICOM | Download requires NBIA Data Retriever |
422 | 422 | 1,265 | 52,073 | CC BY-NC 3.0 | View |
| Lung1 clinical | Classification, Diagnosis, Demographic, Follow-Up | CSV | CC BY-NC 3.0 | — |
Additional Resources for this Dataset
The NCI Cancer Research Data Commons (CRDC) provides access to additional data and a cloud-based data science infrastructure that connects data sets with analytics tools to allow users to share, integrate, analyze, and visualize cancer research data.
- Imaging Data Commons (IDC) (Imaging Data)
- IDC Zenodo community dataset AI-derived annotations for the NLST and NSCLC-Radiomics computed tomography imaging collections
Citations & Data Usage Policy
Data Citation Required: Users must abide by the TCIA Data Usage Policy and Restrictions. Attribution must include the following citation, including the Digital Object Identifier:
Data Citation |
|
|
Aerts, H. J. W. L., Wee, L., Rios Velazquez, E., Leijenaar, R. T. H., Parmar, C., Grossmann, P., Carvalho, S., Bussink, J., Monshouwer, R., Haibe-Kains, B., Rietveld, D., Hoebers, F., Rietbergen, M. M., Leemans, C. R., Dekker, A., Quackenbush, J., Gillies, R. J., Lambin, P. (2014). Data From NSCLC-Radiomics (version 4) [Data set]. The Cancer Imaging Archive. https://doi.org/10.7937/K9/TCIA.2015.PF0M9REI |
Detailed Description
Radiation Oncologist Tumor Segmentations
The DICOM Radiotherapy Structure Sets (RTSTRUCT) and DICOM Segmentation (SEG) files in this data contain a manual delineation by a radiation oncologist of the 3D volume of the primary gross tumor volume (“GTV-1”) and selected anatomical structures (i.e., lung, heart and esophagus). Of note, DICOM SEG objects contain a subset of annotations available in RTSTRUCT.
For viewing the annotations the authors recommend 3D Slicer that can be used to view both RTSTRUCT and SEG annotations (make sure you install the SlicerRT and QuantitativeReporting extensions first!). Visualization of the DICOM annotations is also supported by the OHIF Viewer.
Other tools include:
- Dicompyler is an open source, cross-platform DICOM RT viewer.
- The Radiotherapy DICOM toolkit, which may also be useful for working with this data.
- dcmqi and Plastimatch libraries can be used to support conversion of the DICOM SEG and RTSTRUCT representations, respectively, into the popular research formats, such as NIfTI or NRRD.
Clinical Data
Corresponding clinical data can be found here: Lung1.clinical.csv.
Please note that survival time is measured in days from start of treatment. DICOM patients names are identical in TCIA and clinical data file.
The deadstatus.event follows the standard epidemiological / biomedical definition for time to event survival modelling whereby :
1 == “death has occurred at the time interval value stated on the next column”, hence
0 == “death has NOT occurred up until the time interval value stated in the next column, and is therefore right-censored”.
Note:
Some CT ( LUNG1-014 , LUNG1-021 , LUNG1-085) are missing some slices from the complete volume, unfortunately not detected until recently. The skipped CT slice did not cut through the Gross Tumour Volume which was the principal focus of this Collection. We understand the user may have a different principal focus for re-using this collection, but perhaps some other workaround like interpolation may be timely and feasible for those affected volumes.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the individuals and institutions that have provided data for this collection:
- Leonard Wee, MAASTRO (Dept of Radiotherapy), Maastricht University Medical Centre+, Maastricht, Limburg, The Netherlands.
- Dirk de Ruysscher, MAASTRO (Dept of Radiotherapy), Maastricht University Medical Centre+, Maastricht, Limburg, The Netherlands.
- Andre Dekker, MAASTRO (Dept of Radiotherapy), Maastricht University Medical Centre+, Maastricht, Limburg, The Netherlands.
- Hugo Aerts, Computational Imaging and Bioinformatic Laboratory, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute & Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA.
- Harmonization of the components of this dataset, including into standard DICOM representation, was supported in part by the NCI Imaging Data Commons consortium. NCI Imaging Data Commons consortium is supported by the contract number 19X037Q from Leidos Biomedical Research under Task Order HHSN26100071 from NCI.
Related Publications
Publications by the Dataset Authors
The authors recommended the following as the best source of additional information about this dataset:
Publication Citation |
|
|
Aerts, H. J. W. L., Velazquez, E. R., Leijenaar, R. T. H., Parmar, C., Grossmann, P., Carvalho, S., Bussink, J., Monshouwer, R., Haibe-Kains, B., Rietveld, D., Hoebers, F., Rietbergen, M. M., Leemans, C. R., Dekker, A., Quackenbush, J., Gillies, R. J., Lambin, P. (2014, June 3). Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nature Communications. Nature Publishing Group. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5006 (link) |
.
Research Community Publications
TCIA maintains a list of publications that leveraged this dataset. If you have a manuscript you’d like to add please contact TCIA’s Helpdesk.
Previous Versions
Version 3: Updated 2019/10/23
- Re-checked and updated the RTSTRUCT files to amend issues in the previous submission due to missing RTSTRUCTS or regions of interest that were not vertically aligned with the patient image.
- In 4 cases (LUNG1-083,LUNG1-095,LUNG1-137,LUNG1-246) re-submitted the correct CT images.
- The regions of interest now include the primary lung tumor labelled as “GTV-1”, as well as organs at risk.
- For one case (LUNG1-128) the subject does not have GTV-1 because it was actually a post-operative case; we retained the CT scan here for completeness.
- Added DICOM SEGMENTATION objects to the collection, which makes it easier to search and retrieve the GTV-1 binary mask for re-use in quantitative imaging research.
- Clinical data updated as follow-up time has been extended.
| Title | Data Type | Format | Access Points | License | Metadata | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Images | CT | DICOM | Download requires NBIA Data Retriever |
422 | 422 | 422 | 51,230 | — | |
| Lung1 clinical | CSV | — |
Version 2: Updated 2016/05/31
Added 318 RTSTRUCT files for existing subject imaging data. (NOTE: version 2 removed as RTSTRUCTs or regions of interest were not vertically aligned with patient images. See version 3 for updated files).
| Title | Data Type | Format | Access Points | License | Metadata | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Images | DICOM | — | |||||||
| Lung1 clinical | CSV | — |
Version 1: Updated 2014/07/02
| Title | Data Type | Format | Access Points | License | Metadata | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Images | CT | DICOM | Download requires NBIA Data Retriever |
422 | 422 | 422 | 51,230 | — | |
| Lung1 clinical | CSV | — |