QIN PET Phantom | QIN PET Phantom
DOI: 10.7937/k9/tcia.2015.zpukhckb | Data Citation Required | 428 Views | 2 Citations | Image Collection
| Location | Species | Subjects | Data Types | Cancer Types | Size | Status | Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phantom | Human | 2 | PT, Other | Phantom | Public, Complete | 2014/09/04 |
Summary
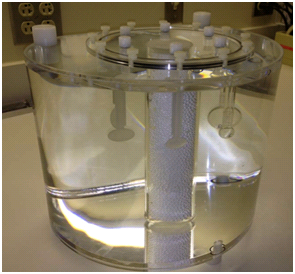
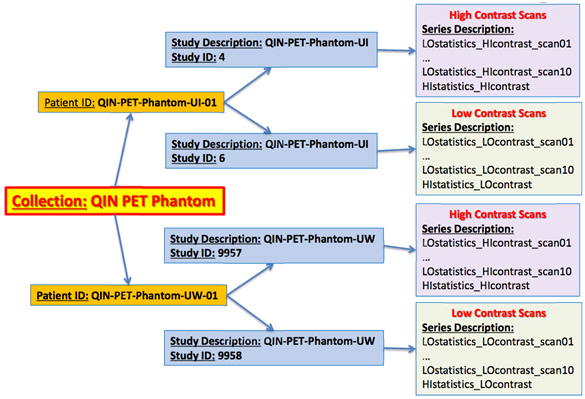
This collection consists of positron emission tomography (PET) phantom scans originally utilized by the Quantitative Imaging Network (QIN) PET Segmentation Challenge to assess the variability of segmentations and subsequently derived quantitative analysis results on phantom PET scans with known ground truth.The phantom was provided by Dr. Sunderland at the University of Iowa (supported by grant R01CA169072 - Harmonized PET Reconstructions for Cancer Clinical Trials) and is based on the NEMA IEC Body Phantom SetTM (Model PET/IEC-BODY/P) with a set of 6 custom made (via rapid prototyping) spheres & ellipses (Fig. 1). The phantom was scanned at two QIN sites (University of Iowa and University of Washington) with different scanners, following a protocol that yields four image sets (Fig. 2) per site. The DICOM PET images are organized as shown in Fig. 3. These figures are located in the Detailed Description tab below. The mission of the QIN is to improve the role of quantitative imaging for clinical decision making in oncology by developing and validating data acquisition, analysis methods, and tools to tailor treatment for individual patients and predict or monitor the response to drug or radiation therapy. More information is available on the Quantitative Imaging Network Collections page. Interested investigators can apply to the QIN at: Quantitative Imaging for Evaluation of Responses to Cancer Therapies (U01) PAR-11-150.About the NCI QIN
Data Access
Version 1: Updated 2014/09/04
| Title | Data Type | Format | Access Points | Subjects | License | Metadata | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Images | PT | DICOM | Download requires NBIA Data Retriever |
2 | 4 | 44 | 2,816 | CC BY 3.0 | View |
| DICOM Metadata Digest | Other | CSV | CC BY 3.0 | — |
Citations & Data Usage Policy
Data Citation Required: Users must abide by the TCIA Data Usage Policy and Restrictions. Attribution must include the following citation, including the Digital Object Identifier:
Data Citation |
|
|
Beichel, R., Ulrich, E. J., Bauer, C., Byrd, D. W., Muzi, J. P., Muzi, M., Kinahan, P. E., Sunderland, J. J., Graham, M. M., & Buatti, J. M. (2015). QIN PET Phantom [Data set]. The Cancer Imaging Archive. https://doi.org/10.7937/k9/tcia.2015.zpukhckb |
Related Publications
Publications by the Dataset Authors
The authors recommended the following as the best source of additional information about this dataset:
No other publications were recommended by dataset authors.
Research Community Publications
TCIA maintains a list of publications that leveraged this dataset. If you have a manuscript you’d like to add please contact TCIA’s Helpdesk.